 Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It occurs in teens and adults and affects both men and women.
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It occurs in teens and adults and affects both men and women.
Trichomonads (how they look under a microscope):
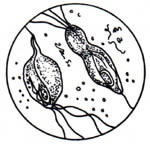
What causes trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is caused by a single-cell parasite called a trichomonad. The parasite is spread through sexual intercourse, so it’s an STI.
Who is a risk for trichomoniasis?
Approximately 3.7 million people in the United States are infected with trichomoniasis. During sex, the parasite is transferred from one person to another. The parasite can be passed on from penis to vagina, vagina to penis, or vagina to vagina. It’s NOT spread by toilet seats.
The parasite infects the urethra (the canal that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body) inside the penis of men and the vulva, vagina and urethra of women. It is uncommon for the parasite to infect other parts of the body, such as hands, mouth, or anus. Most people with trichomoniasis do not have symptoms, so they may not get treated and may spread the infection to their partners.
What are some signs/symptoms of trichomoniasis?
Some symptoms in men may include:
- Burning after urination
- Burning after ejaculation
- Itching/irritation inside the penis (urethra)
Because guys don’t usually show signs of trichomoniasis, it’s important that if you have a female partner, she lets you know if she is experiencing symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge with odor, itching and burning, painful urination or intercourse, or has just been diagnosed with trichomoniasis.
How can a health care provider tell if I have trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can be diagnosed by checking a urine sample for the parasite, or doing other special trichomonas DNA tests.
Are there complications of trichomoniasis?
Having trichomoniasis can increase your risk of getting or spreading other sexually transmitted infections. For example, having trichomoniasis can cause genital inflammation, which can make it easier to get infected with or spread HIV to a sexual partner.
How is trichomoniasis treated?
If you’re diagnosed with trichomoniasis, your health care provider will give you a prescription for a specific antibiotic (most commonly metronidazole or tinidazole) for both you and your female sexual partner(s). You and your female partner(s) should let your health care provider know about any other medications that you’re taking.
Medication for trichomoniasis is only available by prescription. You and your female partner(s) each need to take the whole dose of the medication for it to be the most effective. It’s common to give the prescription in a single dose. Don’t drink alcohol for 24 hours after taking metronidazole or 72 hours after taking tinidazole, or you’ll feel very sick or vomit.
If you take all of the antibiotic dose, trichomoniasis is usually cured. You and your female partner(s) should avoid sexual intercourse until both of you are completely cured. You can be infected again if you don’t take the proper precautions to prevent an STI.
How can trichomoniasis be prevented?
The only way to prevent trichomoniasis completely is to not have sex. If you’re going to have sex, a latex condom is the most effective way to lower your risk of getting trichomoniasis and other STIs.
Additional Information:
Trichomoniasis: CDC Fact Sheet
Source: Read Full Article
