In a recent study published on the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers carried out an analytical susceptibility test with cultured severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant in seven antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic (Ag-RDTs).
Study: Analytical sensitivity of seven SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid tests for Omicron variant. Image Credit: Roman Zaeits / Shutterstock.com
Background
The emergence of a new SARS-CoV-2 VOC necessitates a study of its potential impact on diagnostic performance. The SARS-CoV-2 Ag-RDT is advantageous for its ability to provide rapid results, low cost, and remain independent of the laboratory at the point of care. While the sensitivity of the Ag-RDT is less when compared to the gold standard reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay, this method enables reliable detection of high viral loads associated with the presence of infectious viruses.
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant was reported for the first time in November 2021 in South Africa and is characterized by a large number of mutations as compared to other circulating variants. Apart from the vast number of spike mutations, the Omicron variant also has mutations in the nucleocapsid protein, which is the target of almost all Ag-RDTs.
Two mutations found in Omicron, including the R203K and G204R have already been described in some sequences of SARS-CoV-2 and have been related to increased sub-genomic ribonucleic acid (RNA) and increased viral loads. Additionally, the Del31-33 deletion is found in the Omicron nucleocapsid protein, along with another P13L mutation, which is present in some but not all Omicron sequences. Information on the potential impact of these mutations on the performance of Ag-RDTs is not yet available.
About the study
In the current study, the analytical sensitivity of the cultured virus to the Omicron variant and compared it to data previously obtained on other SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) including the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta variants, as well as a pre-VOC isolate of SARS-CoV-2 using seven Ag-RDTs.
All viruses were isolated from clinical samples and were cultivated in Vero-E6 cells. The Omicron variant, initially isolated on the Vero-TMPRSS cells, was then crossed by a stock passage (p2) prepared on VeroE6. The original patients’ sequence, as well as the virus isolate of the passage, had the following mutations and deletion in the nucleocapsid: R203K, G204R, P13L, and Del31-33.
The researchers followed the manufacturers’ instructions to perform all Ag-RDT assays, with the exception of the addition of a five microliter (μL) virus dilution into the proprietary buffer, and then applied to the Ag-RDT in duplicates under Biological Safety Laboratory 3 (BSL3) conditions. Ag-RDT buffer with no virus was used as a negative control. The visible test band in the presence of a visible control band was considered positive.
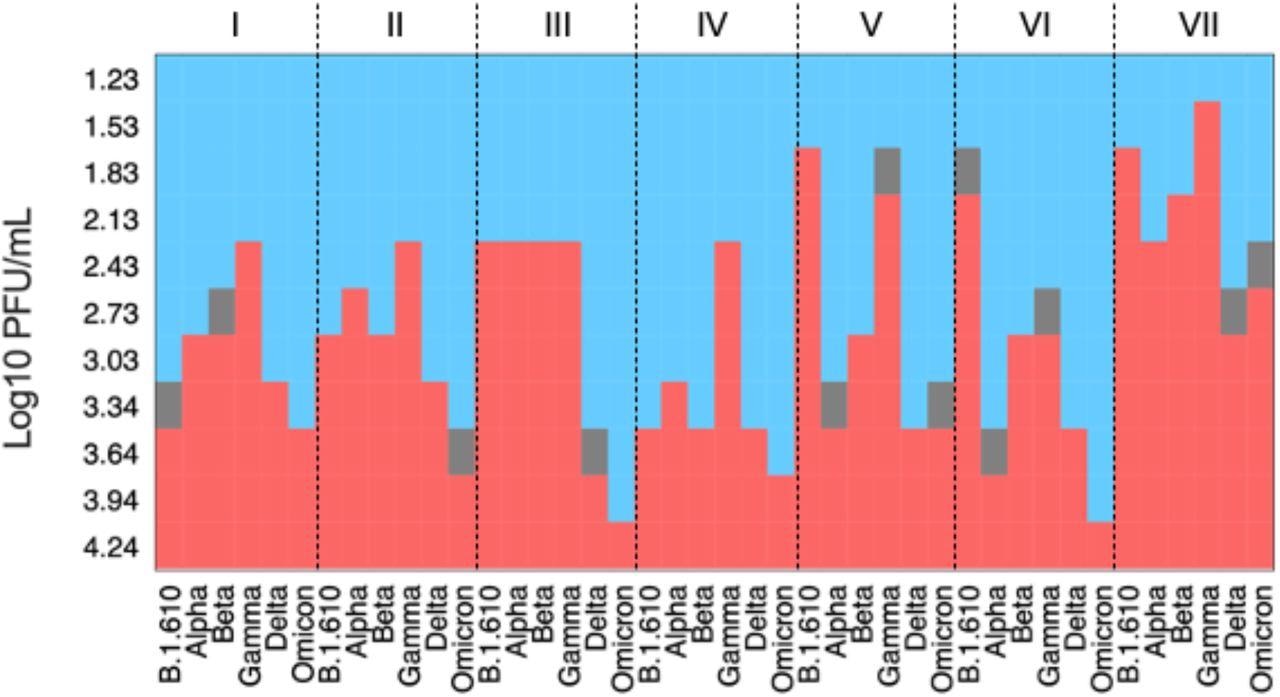
Heat map based on Log10 PFU/mL for analytical sensitivity of seven Ag-RDTs assays with an early-pandemic SARS-CoV-2 isolate (B.1.610), the VOCs Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta in comparison Omicron. Ag-RDTs used: I) Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid test device (Abbott); II) Standard Q COVID-19 Ag (SD Biosensor/Roche); III) Sure Status (Premier Medical Corporation); IV) 2019-nCoV Antigen test (Wondfo); V) Beijng Tigsun Diagnostics Co. Ltd (Tigsun); VI) Onsite COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test (CTK Biotech); VII) Flowflex (ACON Biotech). Analytical sensitivity for early-pandemic SARS-CoV-2 B.1.610, Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta have already been published before but were added here for consistency reasons and better interpretability of the data on Omicron.
Study findings
The analytical sensitivity to detect the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant was lower than that for the other VOCs in most of the tests evaluated. The highest overall sensitivity for all SARS-CoV-2 used was shown by Flowflex, which detected Omicron with slightly higher sensitivity than Delta variant but lower than Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and pre-VOC SARS-CoV-2 strains.
In this analytical method using a cultured virus, considerable heterogeneity in sensitivity patterns across variants and between individual assays was also observed. The mutations in the nucleocapsid protein potentially affected the different epitopes used in each test, which might explain the differences in analytical sensitivity between Ag-RDTs.
Conclusions
While analytical tests with a cultured virus may be a substitute for clinical sensitivity, they are not a substitute for clinical evaluations and have various limitations. The relationship between infectious viruses, viral proteins, and RNA may differ between patient specimens and virus isolates in culture.
Other factors such as in vivo excretion of infectious viruses and overall viral load could further influence the performance of clinical trials. As a result, additional studies on the diagnostic accuracy of Ag-RDTs for the new Omicron VOC are urgently required to inform public health responses.
*Important notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
- Bekliz, M., Adea, K., Alvarez, C., et al. (2021). Analytical sensitivity of seven SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid tests for Omicron variant. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.12.18.21268018. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.18.21268018v1
Posted in: Device / Technology News | Medical Science News | Medical Research News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: Antigen, Assay, Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Diagnostic, Diagnostics, Genomic, in vivo, Laboratory, Mutation, Polymerase, Polymerase Chain Reaction, Protein, Public Health, Respiratory, Ribonucleic Acid, RNA, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Syndrome, Virus

Written by
Saurabh Chaturvedi
Saurabh Chaturvedi is a freelance writer from Jaipur, India. He is a gold medalist in Masters in Pharmaceutical Chemistry and has extensive experience in medical writing. He is passionate about reading and enjoys watching sci-fi movies.
Source: Read Full Article
