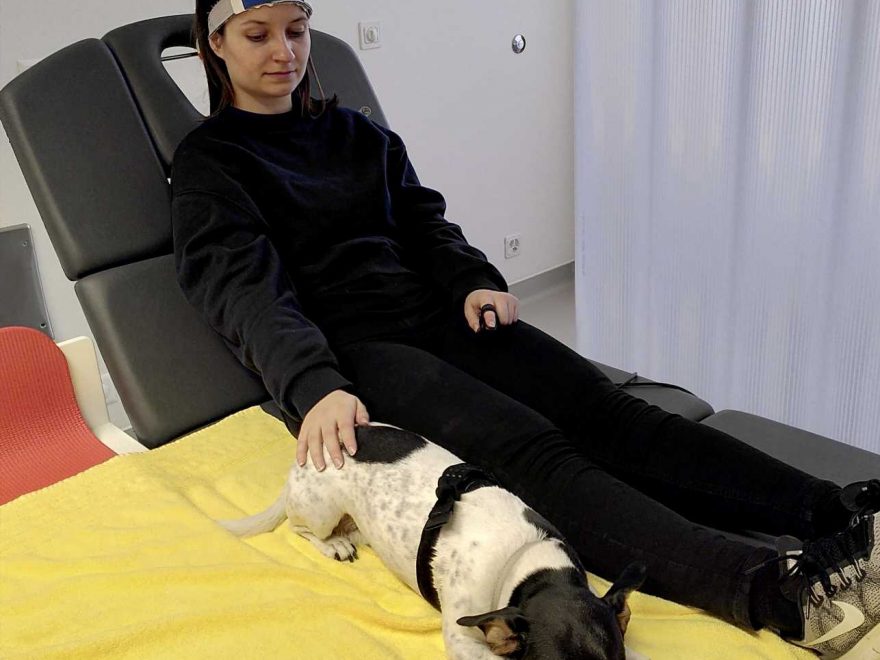
Researchers led by Rahel Marti at the University of Basel in Switzerland report that viewing, feeling, and touching real dogs leads to increasingly higher levels of activity in the prefrontal cortex of the brain. Published in PLOS ONE on October 5, the study shows that this effect persists after the dogs are no longer present, but is reduced when real dogs are replaced with stuffed animals. The findings have implications for animal-assisted clinical therapy.
Because interacting with animals, particularly dogs, is known to help people cope with stress and depression, researchers think that a better understanding of the associated brain activity could help clinicians design improved systems for animal-assisted therapy. The prefrontal cortex might be particularly relevant because it helps regulate and process social and emotional interactions.
In the study, activity in the prefrontal cortex of the brain was non-invasively measured with infrared neuroimaging technology as 19 men and women each viewed a dog, reclined with the same dog against their legs, or petted the dog. Each of these conditions was also performed with Leo, a stuffed lion with fur that was filled with a water bottle to match the temperature and weight of the dogs.
Results showed that prefrontal brain activity was greater when participants interacted with the real dogs, and that this difference was largest for petting, which was the most interactive condition. Another key difference was that prefrontal brain activity increased each time people interacted with the real dog. This was not observed with successive interactions with the stuffed lion, indicating that the response might be related to familiarity or social bonding.
Future studies will be needed to examine the issue of familiarity in detail and whether petting animals can trigger a similar boost of prefrontal brain activity in patients with socioemotional deficits.
Source: Read Full Article