A significant percentage of COVID-19 cases are severe enough to warrant admission to hospital for monitoring and treatment. A substantial number of these patients die from the disease after appearing to respond well to treatment. The major cause of these deaths is a phenomenon called the cytokine storm, which occurs when hyperactivation of immune cells leads to a large amount of cytokines (cell signaling molecules), which in turn trigger systemic hyperinflammation. If untreated, this leads to multiple organ failure and, finally, death. If the cytokine storm could be weakened or prevented, the number of mortalities due to this phenomenon would drastically decrease, reducing the overall mortality to COVID-19.
Ryo Otsuka and Ken-ichiro Seino from the Institute for Genetic Medicine (IGM) at Hokkaido University reviewed the existing research on macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). Their work, published in the journal Inflammation and Regeneration, addresses the role that MAS plays in COVID-19, and highlights how existing therapies for MAS have shown initial success in ameliorating severe COVID-19 cases.
The cytokine storm occurs in other diseases and disorders such as influenza, pneumonia and sepsis, and has been studied in some detail. Along with MAS, an associated syndrome is the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which is characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs—a common feature of severe COVID-19 cases. Thus, the scientists reviewed the links between MAS and ARDS and the role MAS played in COVID-19.
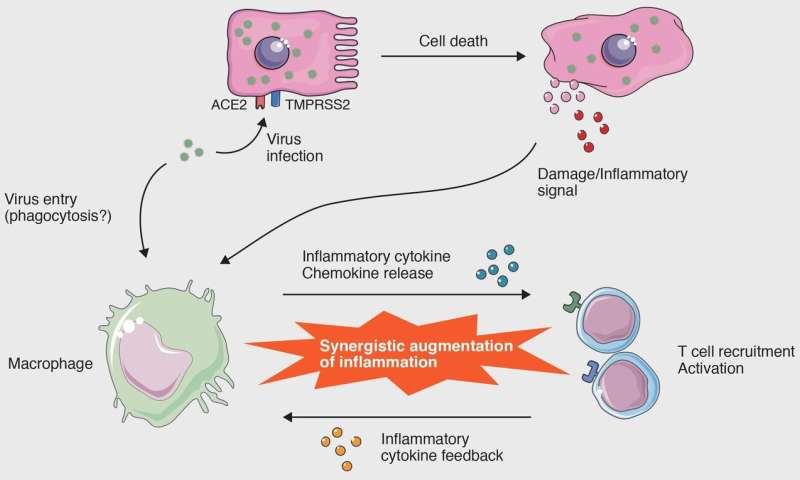
Their review explained that MAS in COVID-19 was accompanied by ARDS, and that far more cytokines were involved than in previously documented cases of MAS. This difference is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. When the virus enters the cells, it triggers an inflammatory response as the cells fight against it. The virus also triggers the inflammatory response by causing pyroptosis (a type of cell death caused when it infects cells), which activates macrophages. Additionally, the virus enters macrophages, activating them. The activated macrophages recruit T cells, which activate more macrophages, triggering a positive feedback loop. This causes MAS, which in turn leads to ARDS—which, untreated, is fatal.
According to this review, MAS is directly triggered by cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα), and indirectly by IL-1. The scientists discussed previous case studies that had used therapies targeting these molecules to suppress MAS.
Source: Read Full Article
