With the help of cerebral organoids, IMBA scientists were able to ascertain that tuberous sclerosis, a rare neurodevelopmental genetic disorder, arises developmentally rather than only genetically. With these patient-derived laboratory models of the human brain, they pinpointed the origin of the disease to progenitor cells specific to humans. The findings, now published in Science, further show that the pathology of diseases affecting the human brain could only be well understood using human-derived brain organoid models.
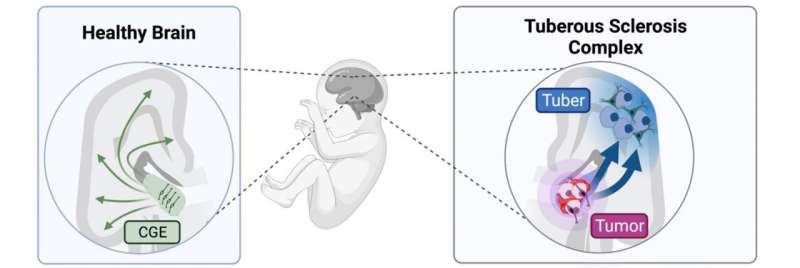
The complexity of the human brain is largely due to development involving processes unique to humans, many of which are still lurking in the darkest corners of our current scientific knowledge. Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is no exception in this respect, as it has long been described as a chiefly genetic disorder based on data obtained from animal models. Now, breakthrough research from the Knoblich lab at IMBA—Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences—uses patient-derived cerebral organoid models to pierce the mysteries of this rare neurodevelopmental disease. “Our findings on the root cause of TSC led us to a progenitor cell type specific to the human brain. This explains why the pathology of this disease could not be well established with other laboratory models,” explains IMBA Scientific Director Jürgen Knoblich, co-corresponding author on the publication.
In many affected patients, TSC manifests in the form of severe epilepsy and psychiatric symptoms like autism and learning difficulties. Morphologically, TSC is characterized by well-described signs often found in the brains of patients. Among those are benign tumors present in a defined area of the brain, as well as lesions in the cortex, called “tubers.” For a long time, both morphological aberrations have been attributed to a genetic cause. However, results from the analysis of patient samples diverged from the prevalent theory, mainly with regards to tubers. “To study tuberous sclerosis, we developed cerebral organoid models of the disease: three-dimensional cell cultures that we use to model the brain and that we can derive from any patient,” explains co-corresponding author Nina Corsini, Research Associate in the Knoblich Group at IMBA.
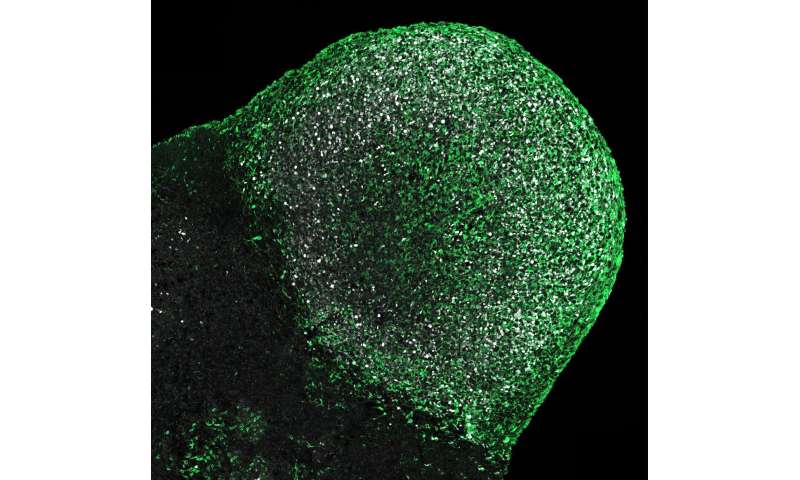
For the study led by Corsini and Knoblich, the team grew brain organoids from several affected patients, a method that allows to investigate molecular and cellular mechanisms that existed in the patients’ brains at some point during development. “With this approach, we found that, like in the patients’ brains, the organoids grew tumors and had disorganized areas that resembled patient tubers,” explains Oliver Eichmüller, the first author on the study.
However, recapitulating the pathophysiology of a disease is only the first step: “By digging further into the causes, we found that both of these abnormalities were triggered by the excessive proliferation of a cell type specific to the human brain,” says Eichmüller. These cells were termed caudal late interneuron progenitors, or CLIP cells. They are found during the developmental stage of human brains, but not in animals like mice. “Our study shows that our brain is very complex—much more complex than the brains of most animals,” says Corsini.
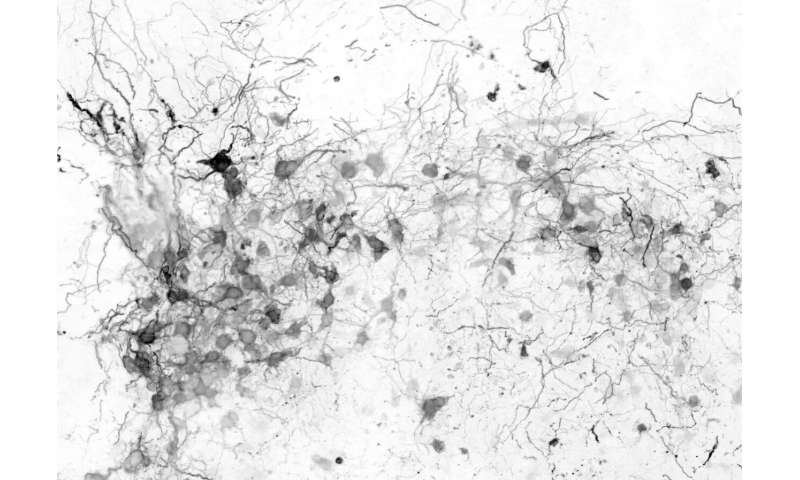
The scientists draw parallels to other neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric diseases, but also to malignant diseases affecting human brains, speculating that these could also be caused by human-specific developmental processes. “Our findings on human-specific principles in brain development and pathology could also apply to other known diseases for which no therapies exist to date,” states Knoblich.
Source: Read Full Article
