Researchers from the Prostate Cancer Biology laboratory, directed by Giuseppina Carbone, M.D., at the Institute of Oncology Research (IOR, affiliated to USI) in Bellinzona, have discovered an unexpected mechanism that drives the largest group of prostate tumors’ evolution, the ERG fusion-positive prostate cancers. The study is published in Nature Communications.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies and causes of mortality in men worldwide. About 50% of prostate tumors (ERG fusion-positive prostate cancers) harbor a fusion between the ERG gene and the promoter region of TMPRSS2 gene. This chromosomal rearrangement leads to abnormal production of ERG and promotes tumor progression. However, the mechanism by which ERG contributes to the tumorigenesis and drives the progression from primary to metastatic and hormone-refractory prostate cancers is still unclear.
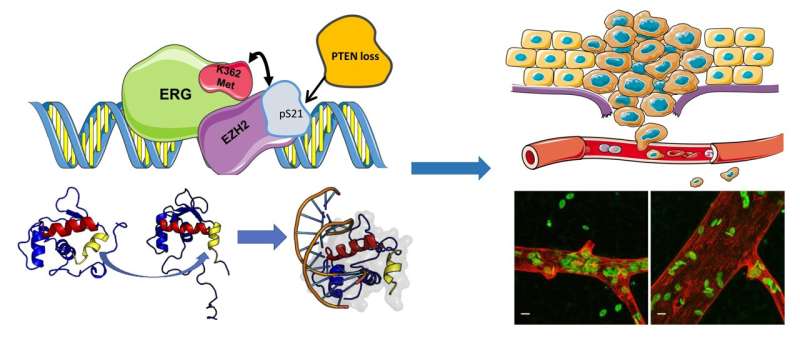
Looking for proteins that potentially interact and cooperate with ERG, researchers identified EZH2. Dr. Carbone explains: “We discovered that EZH2 binds and adds a methyl group to ERG, acting as a co-activator. EZH2 is a partner-in-crime of ERG in prostate cancer progression.”
The researchers observed that the addition of a methyl group on a specific site of ERG was enhancing its tumorigenic activity. “The methylation of lysine 362 is like a switch turning ERG from a quiescent to a very active state. This modification occurs in a critical position at the boundary of an internal auto-inhibitory domain in the ERG protein,” says Dr. Cavalli.
With the methylation on lysine 362, ERG changes its conformation and increases its activity, promotig the expression of multiple genes involved in tumor progression and metastasis. Using preclinical models of ERG fusion-positive prostate cancer, the researchers unraveled the role of another important player in EZH2-ERG activation: the gene PTEN. Deletion of PTEN are widespread in prostate cancers and often associated with ERG fusion-positive tumors. Dr. Carbone’s group observed that the loss of PTEN increased EZH2 activity and, therefore ERG methylation, thus explaining the combined effects of these events in patients.
Source: Read Full Article
